Monday marks four years since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the COVID-19 outbreak a pandemic.
Since the first cases in Wuhan, China, in 2019, there have been millions of infections and deaths around the world.
There have also been major successes including vaccines for nearly all age groups, the development of antiviral drugs to treat those at risk of severe illness and the proliferation of at-home tests.
ABC News takes a look back at the some of the most important moments over the last four-plus years:
Dec. 31, 2019
The World Health Organization office in China is notified about a mysterious pneumonia-like illness that originated in Wuhan and has been spreading.
Jan. 7, 2020
Chinese public health officials identify a new type of coronavirus as the source of the outbreak.

In this Jan. 17, 2020, file photo, medical staff transfer patients to Jin Yintan hospital in Wuhan, Hubei, China, after a second person in the city had died of a pneumonia-like virus since the outbreak started in December.
Getty Images, FILE
Jan. 10, 2020
WHO begins using 2019-nCoV to refer to the outbreak. Because the disease is similar to the SARS virus, it is called SARS-CoV-2.
Jan. 20, 2020
The U.S. confirms its first case in a man in his 30s in Washington state, who developed symptoms after a trip to Wuhan.
Jan. 30, 2020
The WHO declares the outbreak of the virus to be a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirms person-to-person transmission in the U.S.
Feb. 11, 2020
The WHO proposes calling the disease caused by the virus COVID-19, which stands for coronavirus disease 2019.
March 11, 2020
The WHO classifies COVID-19 as a pandemic.
March 13, 2020
President Donald Trump declares the COVID-19 outbreak a national emergency.
March 19, 2020
The U.S. Department of State issues a global Level 4 “Do Not Travel” health advisory.
April 2, 2020
More than 1 million people worldwide have confirmed cases of COVID-19.
April 3, 2020
The CDC announces new guidelines for mask wearing and advises all Americans to wear a mask outside of the home.
May 15, 2020
President Trump announces Operation Warp Speed, a national program to fast-track the development, manufacturing and distribution of COVID-19 tests, treatments and vaccines.
May 28, 2020
The U.S. surpasses 100,000 COVID-19 deaths, a little more than four months after confirming the first known case.
Aug. 6, 2020
The State Department lifts the global Level 4 “Do Not Travel” health advisory.

In this March 11, 2020, file photo, World Health Organization Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus speaks at a press conference in Geneva, Switzerland, announcing that the COVID-19 outbreak can be characterized as a “pandemic” as the virus spreads increasingly worldwide.
Xinhua via Getty Images, FILE
Aug. 28, 2020
The first case of COVID-19 reinfection in the U.S. is reported by the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
Sept. 28, 2020
Global COVID-19 deaths surpass 1 million.
Dec. 11, 2020
FDA grants Pfizer-BioNTech the first EUA for a COVID-19 vaccine for those aged 16 and older.
Dec. 14, 2020
Nurse Sandra Lindsay is the first person to receive a COVID-19 vaccine in the U.S. as distribution begins.
Dec. 18, 2020
The FDA grants the same EUA to Moderna for its vaccine for those aged 18 and older.
Jan. 12, 2021
The CDC says all air passengers entering the U.S. must present a negative COVID-19 test result.

In this Dec. 14, 2020, file photo, Sandra Lindsay, a nurse at Long Island Jewish Medical Center, is inoculated with the COVID-19 vaccine by Dr. Michelle Chester, in Queens, New York.
Pool via Getty Images, FILE
Feb. 27, 2021
The FDA issues an EUA for the Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine for those aged 18 and older.
May 10, 2021
The FDA expands the EUA for the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine to adolescents between ages 12 and 15.
May 13, 2021
CDC guidance is updated for fully vaccinated people, ending indoor mask requirements.
May 26, 2021
President Joe Biden issues a statement saying the U.S. intelligence community cannot determine whether COVID-19 originated in animals and jumped to humans or came from a laboratory accident, with some believing the former and others the latter.
Aug. 12, 2021
The FDA amends EUA for Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna COVID-19 vaccines to authorize additional booster for certain groups with weakened immune systems.
Sept. 22, 2021
The FDA authorizes a booster dose of Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for certain groups.
Oct. 6, 2021
The WHO publishes a clinical case definition of “post COVID-19 condition” or long COVID.
Oct. 20, 2021
The FDA authorizes a booster dose of the Moderna and J&J COVID-19 vaccines for certain groups.
Oct. 29, 2021
The FDA authorizes emergency use of Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine for children ages 5 to 11.
Nov. 8, 2021All non-citizens who are traveling to the U.S. are now required to be fully vaccinated and provide proof of their vaccination status to fly to the U.S., the White House announces. All travelers will continue to be required to show a negative pre-departure COVID-19 test taken no more than three days before they board their flights.
Nov. 19, 2021
The CDC updates guidance to recommend everyone aged 18 and older to get a COVID-19 booster.
Dec. 9, 2021
The FDA expands eligibility to allow 16- and 17-year-olds to receive the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 boosters.
Dec. 22-23, 2021
The FDA issues EUA for two oral antivirals to treat COVID-19 — Merck’s molnupiravir and Pfizer’s Paxlovid — for those with mild to moderate illness at high risk of severe disease.
Jan. 3, 2022
The FDA expands the EUA for Pfizer-BioNTech’s booster to include 12-to-15-year-olds and a third primary dose for some immunocompromised children ages 5 to 11.
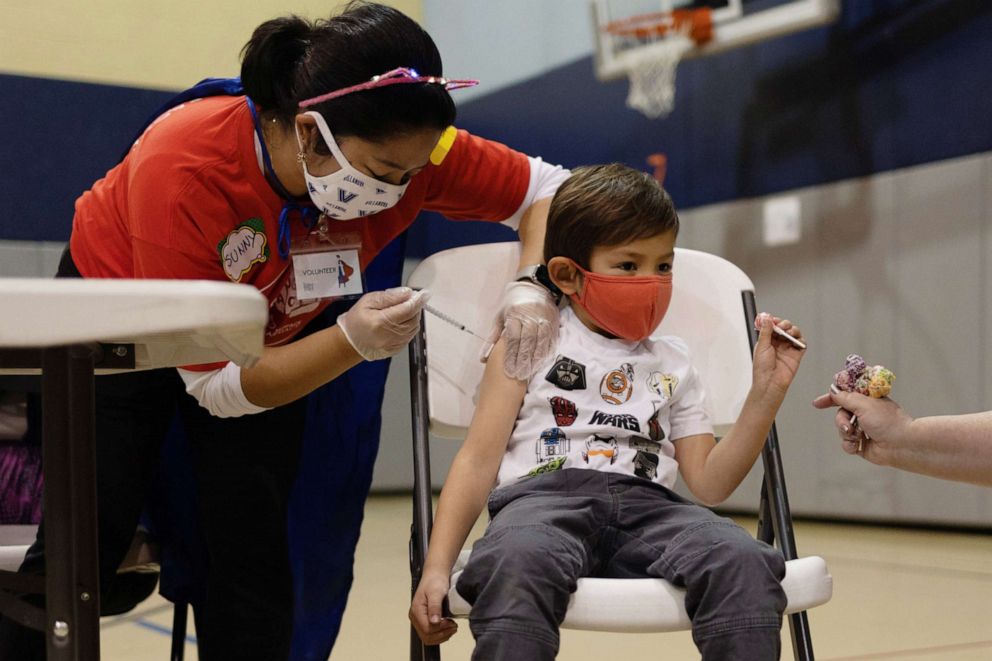
In this Dec. 5, 2021, file photo, a 5-year-old boy receives the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine in Lansdale, Penn.
Hannah Beier/Reuters, FILE
Jan. 4, 2022
The U.S. reports the first day of more than 1 million daily COVID-19 cases during the omicron wave.
Jan. 15, 2022
The U.S. reaches a peak of weekly new hospital admissions for COVID-19 at 150,650 during the omicron wave.
Jan. 18, 2022The White House launches a program to mail at-home COVID-19 tests directly to Americans’ homes with a new website.
March 8, 2022
The Biden administration announces the launch of “Test to Treat” so people at high-risk for developing severe COVID-19 and complications can get tested at a pharmacy and, if positive, receive antiviral pills on the spot for free.
March 29, 2022
The FDA authorizes a second booster dose of either the Pfizer-BioNTech or the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine for people aged 60 and older and certain immunocompromised groups.
May 12, 2022COVID-19 deaths in the U.S. surpass 1 million. President Biden orders flags to be flown at half-staff.
May 17, 2022FDA expands eligibility for a booster dose of Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine to children ages 5 to 11.
June 10, 2022
The CDC rescinds its order requiring a negative COVID-19 test result before boarding a flight to the U.S., taking effect on June 12.
June 17, 2022
The FDA grants EUA for Pfizer-BioNTech’s COVID-19 vaccine for children ages 6 months to 5 years and for Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine for children ages 6 months to 6 years.
Aug. 31, 2022
The FDA authorizes Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna bivalent COVID-19 vaccines to use as a booster dose for those ages 12 and older and those ages 17 and older, respectively.
Oct. 12, 2022
The FDA authorizes an updated bivalent COVID-19 vaccine for children aged 5 and older for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine and for children aged 6 and older for the Moderna vaccine.
Dec. 8, 2022
The FDA authorizes bivalent vaccines to use as a booster dose for children under age 5.
April 10, 2023
President Biden signs H.J.Res.7, ending the national emergency related to the COVID-19 pandemic.
May 5, 2023
The WHO downgrades COVID-19 from being a Public Health Emergency of International Concern but continues to classify it as a pandemic. The CDC says it will no longer track transmission levels.

In this undated file photo, a COVID-19 at home self test kit is shown.
UIG via Getty Images, FILE
Sept. 11, 2023
The FDA authorizes and approves an updated COVID vaccine for all Americans ages 6 months and older.
May 11, 2023
The public health emergency designation in the U.S. for COVID-19 expires.
Nov. 10, 2023
The WHO updates its COVID treatment guidance, including recommending use of the antiviral drugs remdesivir and molnupiravir for only severe cases.
March 1, 2024
People who are recovering from COVID-19 no longer need to remain isolated for five days after symptoms, according to new CDC guidance.
March 10, 2024The Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center stops collecting data for its famous COVID-19 dashboard.

